Airspace Disease Vs Pneumonia
Airspace disease vs pneumonia. It can result from viruses bacteria or fungi. Moreover bilateral involvement 692 was most frequent than unilateral one. It may occur when an injury to the lungs triggers an abnormal healing.
Early in the course of disease CXRs may reveal bulging fissures due to the intense inflammatory exudation present. Most often it occurs as a result of a viral illness such as influenza flu measles or. Her pulmonary artery pressure was.
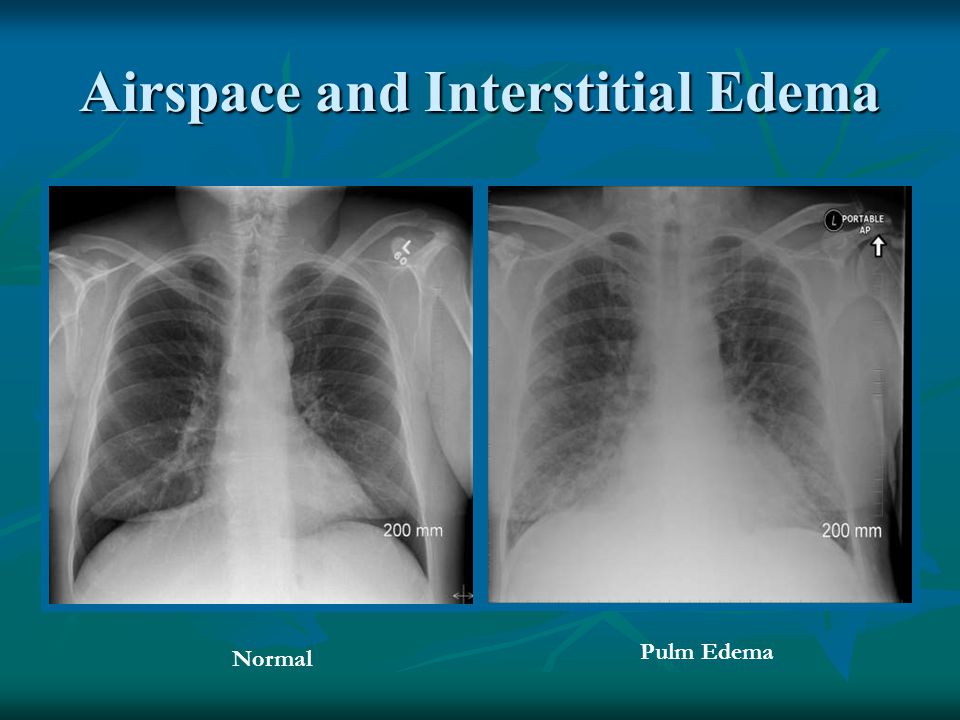
Clinically disease states and environmental factors such as smoking all play a major role in the increase of dead space. Consolidation must be present to diagnose pneumonia. HAPE is a primary hemodynamic problem in the pulmonary arteries and veins Figure whereas in ARDS the edema primarily results from inflammation and alveolar epithelial dysfunction.
It is considered a radiologic sign. We postulate that the nitro-glycerine may have reduced her already attenuated HPV worsening ventilationperfusion matching and leading to decompensation. Alveolar lung disease may be divided into acute or chronic.
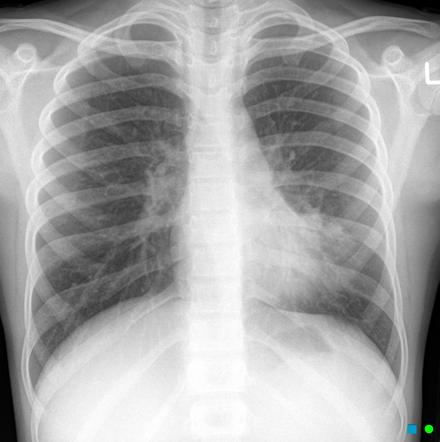
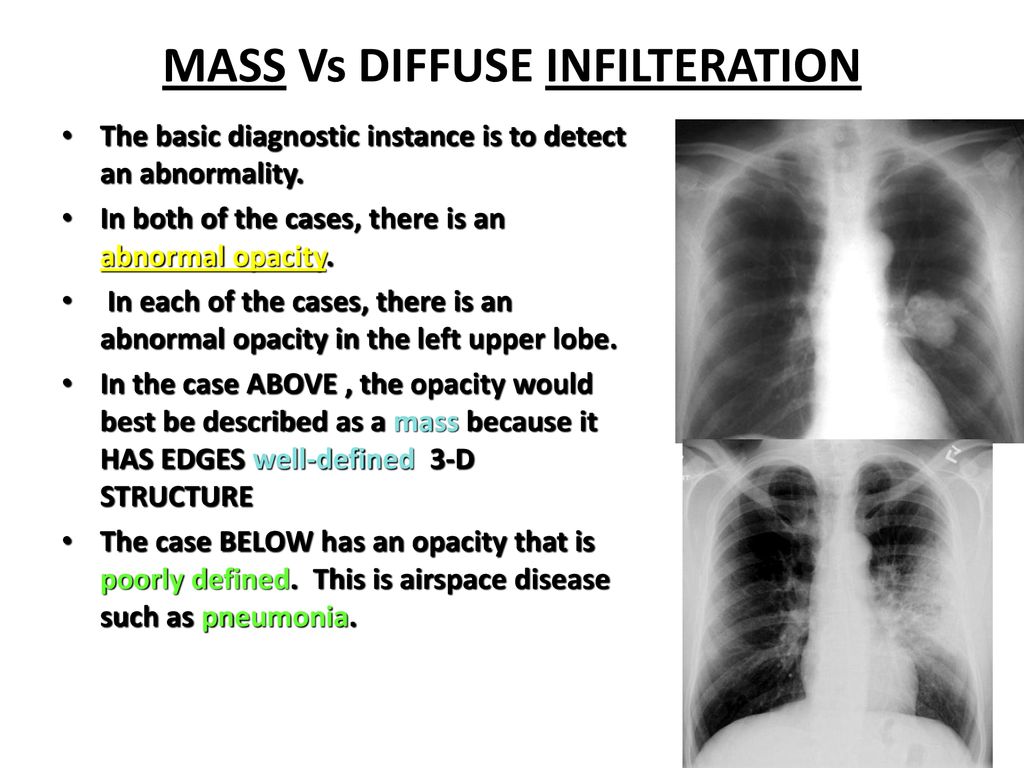
Physical examination on admission revealed a few coarse crackles bilaterally. However since pneumonia is usually associated with an infection some doctors choose to use the term interstitial pneumonitis to refer to inflammation in the interstitial space since many of the causes of this inflammation are not infections. Identifying multifocal air-space disease on CXR can be a significant clue to COVID-19 pneumonia.
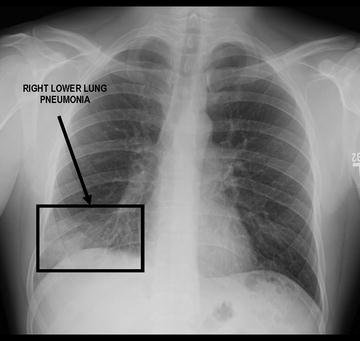
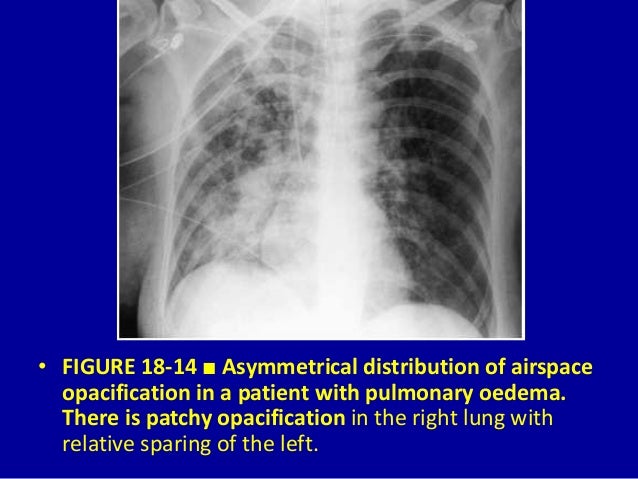
Increases in dead space can be seen in lung disease states including emphysema pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome ARDS. However in chronic disease this segment is subject to considerable variation in size. Airspace opacity overlying the heart more likely to be atelectasis than pneumonia aspiration equivocal atelectasis vs.
Causes of acute alveolar lung disease include pulmonary edema cardiogenic or neurogenic pneumonia bacterial or viral systemic lupus erythematosus bleeding in the lungs eg Goodpasture syndrome idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis and granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Interstitial lung disease ILD or diffuse parenchymal lung disease DPLD is a group of lung diseases affecting the interstitium the tissue and space around the alveoli air sacs of the lungs.
Normally the lingula extends to the diaphragm inferiorly but with processes such as bronchiectasis and interstitial pneumonitis in which atelectasis and fibrosis usually occur contraction results and there is shrinkage toward the left hilus.
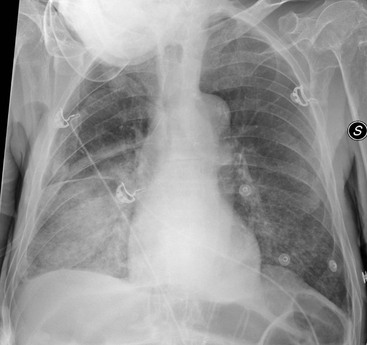
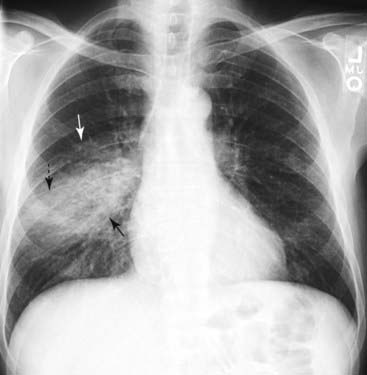
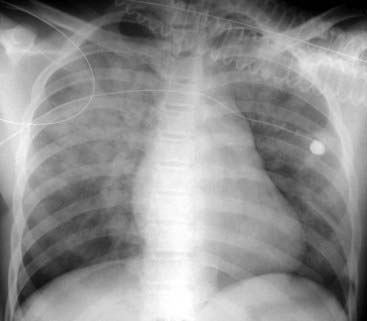
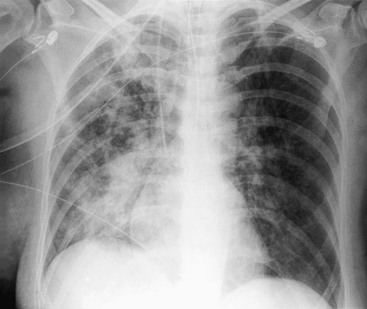
The condition is marked by induration of a normally aerated lung. Increases in dead space can be seen in lung disease states including emphysema pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome ARDS. Multifocal patchy airspace disease consistent with COVID-19 pneumonia figure 1. The condition is marked by induration of a normally aerated lung. Most often it occurs as a result of a viral illness such as influenza flu measles or. A pulmonary consolidation is a region of normally compressible lung tissue that has filled with liquid instead of air. Her pulmonary artery pressure was. Normally the lingula extends to the diaphragm inferiorly but with processes such as bronchiectasis and interstitial pneumonitis in which atelectasis and fibrosis usually occur contraction results and there is shrinkage toward the left hilus. Alveolar lung disease may be divided into acute or chronic.
The liquid can be pulmonary edema inflammatory exudate pus inhaled water or blood. Airspace opacity overlying the heart more likely to be atelectasis than pneumonia aspiration equivocal atelectasis vs. Open in a separate window Fig. Multifocal patchy airspace disease consistent with COVID-19 pneumonia figure 1. Moreover bilateral involvement 692 was most frequent than unilateral one. Causes of acute alveolar lung disease include pulmonary edema cardiogenic or neurogenic pneumonia bacterial or viral systemic lupus erythematosus bleeding in the lungs eg Goodpasture syndrome idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis and granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Normally the lingula extends to the diaphragm inferiorly but with processes such as bronchiectasis and interstitial pneumonitis in which atelectasis and fibrosis usually occur contraction results and there is shrinkage toward the left hilus.


























Post a Comment for "Airspace Disease Vs Pneumonia"